- 166 Posts
- 34 Comments
- usernamesAreTricky@lemmy.mlto
 ·4 months ago
·4 months agoQuite a range of things. It's so many It's hard to list them all. Some of these are more global than others:
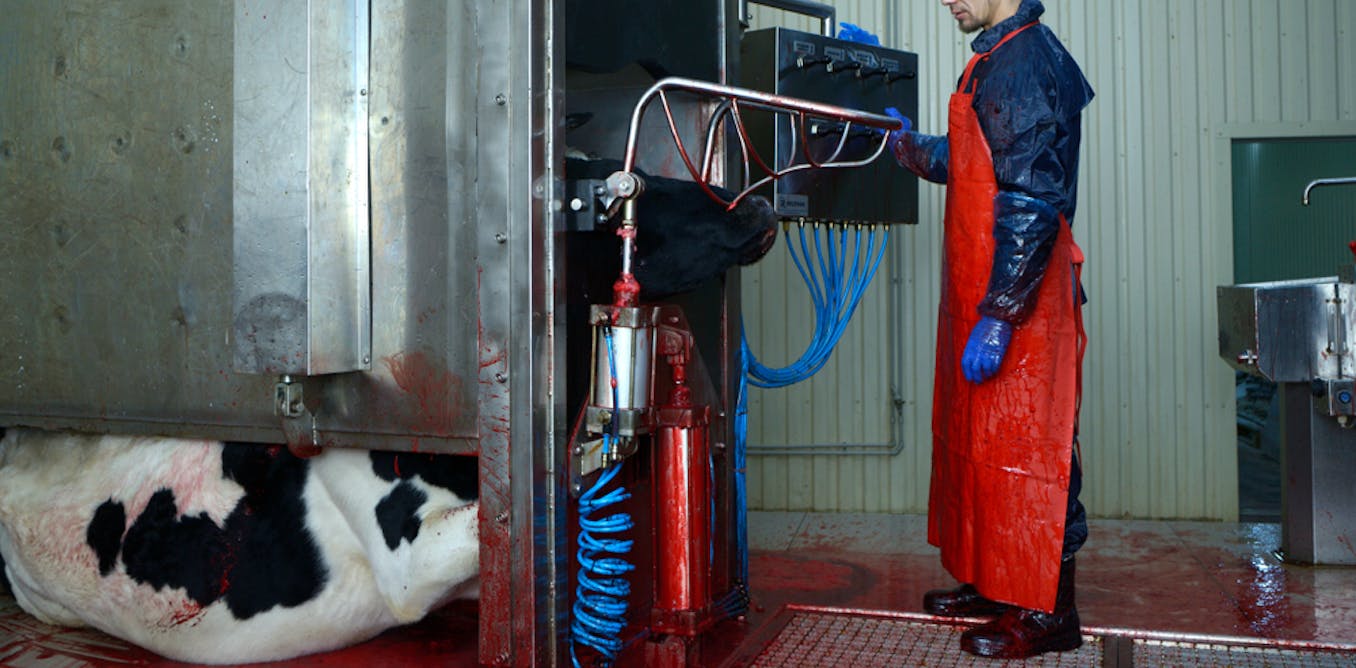
Eyestalk ablation is the removal of one (unilateral) or both (bilateral) eyestalks from a crustacean. It is routinely practiced on female shrimps (or female prawns) in almost every marine shrimp maturation or reproduction facility in the world, both research and commercial.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Eyestalk_ablation
Chick culling or unwanted chick killing is the process of separating and killing unwanted (male and unhealthy female) chicks for which the intensive animal farming industry has no use. It occurs in all industrialised egg production, whether free range, organic, or battery cage.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Chick_culling
A gestation crate, also known as a sow stall, is a metal enclosure in which a farmed sow used for breeding may be kept during pregnancy.[1][2][3] A standard crate measures 6.6 ft x 2.0 ft (2 m x 60 cm).[4][5]
[...]
There were 5.36 million breeding sows in the United States as of 2016, out of a total of 50.1 million pigs.[8] Most pregnant sows in the US are kept in gestation crates.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Gestation_crate
Ventilation shutdown (VSD) is a means to kill livestock by suffocation and heat stroke in which airways to the building in which the livestock are kept are cut off. It is used for mass killing — usually to prevent the spread of diseases such as avian influenza. Animal rights organizations have called the practice unethical.
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ventilation_shutdown
From global estimates
It’s estimated that three-quarters – 74% – of land livestock are factory-farmed
[...]
Combine land animals and fish, and the final estimate comes to 94% of livestock living on factory farms.
https://ourworldindata.org/how-many-animals-are-factory-farmed
- usernamesAreTricky@lemmy.mlto
 ·4 months ago
·4 months agoThe method of mass killing are quite brutal too. In the last outbreaks, primarily these were the two primary methods:
Ventilation shutdown (VSD) is a means to kill livestock by suffocation and heat stroke in which airways to the building in which the livestock are kept are cut off. It is used for mass killing — usually to prevent the spread of diseases such as avian influenza. Animal rights organizations have called the practice unethical. The addition of carbon dioxide or additional heat to the enclosure is known as ventilation shutdown plus (VSD+).[1][2][3][4][5]
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Ventilation_shutdown
Foam depopulation or foaming is a means of mass killing farm animals by spraying foam over a large area to obstruct breathing and ultimately cause suffocation.[1] It is usually used to attempt to stop disease spread.[2] Foaming has also been used to kill farm animals after backlogs in slaughtering occurred during the COVID-19 pandemic.[3] Foam depopulation has been used on poultry and pigs and has seen initial research for use on cattle.[4] It has faced criticism from some groups. Some veterinarians have called it inhumane,[5] along with many animal rights and animal welfare organizations who cite the pain caused by suffocation or the harm experienced by the stray survivors.[6][7]
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Foam_depopulation
- usernamesAreTricky@lemmy.mlto
 ·4 months ago
·4 months agoIt's not just feeding them more that's caused this. To get chickens this large they genetically selected/modified for what was more profitable. I.e they may lead to features being changed unevenly
This is all at expense of pretty everything else like their health
- usernamesAreTricky@lemmy.mlto
 ·5 months ago
·5 months agoThe science doesn't agree with that
It is the position of the Academy of Nutrition and Dietetics that appropriately planned vegetarian, including vegan, diets are healthful, nutritionally adequate, and may provide health benefits for the prevention and treatment of certain diseases. These diets are appropriate for all stages of the life cycle, including pregnancy, lactation, infancy, childhood, adolescence, older adulthood, and for athletes. Plant-based diets are more environmentally sustainable than diets rich in animal products because they use fewer natural resources and are associated with much less environmental damage. Vegetarians and vegans are at reduced risk of certain health conditions, including ischemic heart disease, type 2 diabetes, hypertension, certain types of cancer, and obesity. Low intake of saturated fat and high intakes of vegetables, fruits, whole grains, legumes, soy products, nuts, and seeds (all rich in fiber and phytochemicals) are characteristics of vegetarian and vegan diets that produce lower total and low-density lipoprotein cholesterol levels and better serum glucose control. These factors contribute to reduction of chronic disease
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27886704/
Nevertheless, several RCTs [randomized controlled trials] have examined the effect of vegetarian diets on intermediate risk factors of cardiovascular diseases (Table 1). In a meta-analysis of RCTs, Wang et al. (22) found vegetarian diets to significantly lower blood concentrations of total, LDL, HDL, and non-HDL cholesterol relative to a range of omnivorous control diets. Other meta-analyses have found vegetarian diets to lower blood pressure, enhance weight loss, and improve glycemic control to greater extent than omnivorous comparison diets (23-25). Taken together, the beneficial effects of such diets on established proximal determinants of cardiovascular diseases found in RCTs, and their inverse associations with hard cardiovascular endpoints found in prospective cohort studies provide strong support for the adoption of healthful plant-based diets for cardiovascular disease prevention
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/am/pii/S1050173818300240
Well-planned vegan and other types of vegetarian diets are appropriate for all stages of the life cycle, including during pregnancy, lactation, infancy, childhood, and adolescence. Vegetarian diets offer a number of nutritional benefits, including lower levels of saturated fat, cholesterol, and animal protein as well as higher levels of carbohydrates, fiber, magnesium, potassium, folate, and antioxidants such as vitamins C and E and phytochemicals
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/12778049/
- usernamesAreTricky@lemmy.mlto
 ·5 months ago
·5 months agoAll plant-based foods, whole-foods or not, have lower emissions than animal products
EDIT with a source:
Transitioning to plant-based diets (PBDs) has the potential to reduce diet-related land use by 76%, diet-related greenhouse gas emissions by 49%, eutrophication by 49%, and green and blue water use by 21% and 14%, respectively, whilst garnering substantial health co-benefits
[...]
Plant-based foods have a significantly smaller footprint on the environment than animal-based foods. Even the least sustainable vegetables and cereals cause less environmental harm than the lowest impact meat and dairy products [9].
https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/14/8/1614/htm
- usernamesAreTricky@lemmy.mlto
 ·9 months ago
·9 months agoDoes it disable JS or limit it or something along those lines? Maybe could be the reason?
- usernamesAreTricky@lemmy.mlto
 ·9 months ago
·9 months agoIt should also be noted that we currently do the exact opposite and actually heavily subsidize meat, dairy, etc around the world
- usernamesAreTricky@lemmy.mlto
 ·9 months ago
·9 months agoStrange, doesn't show up like for me. I don't think there's a paywall on this article, so I'm not sure why it'd be showing up like that. Maybe a browser issue? I'm using Firefox, what browser are you using?
Hmm, maybe this could be a DNS issue. Are you using DNS over HTTPS on Firefox (check on
about:preferences#privacy? If so, what do you have the DNS provider set as?Also what happens if you go to a website that is ipv6 only such as https://ip6only.me/? Does it fail to connect or does it then actually use ipv6?
First check if you have ipv6 disabled in Firefox. I think there was a DNS issue on some lemmy instance a while ago where people were turning ipv6 off to work around that (was later fixed) or maybe I am misremembering where that was
Go to
about:configthen make sure thatnetwork.dns.disableIPv6is false.
- usernamesAreTricky@lemmy.mlto
 ·10 months ago
·10 months agoMain idea: They can't restore any color by filtering or let you perceive any new colors as their marketing likes to claim. At best they might be able to improve contrast of certain colors while reducing contrast for others - which is not at all what they say it does
The video goes much more into depth about their deceptive marketing and such
- usernamesAreTricky@lemmy.mlto
 ·1 year ago
·1 year agoThis study looks at the effects more so of replacing red meat with plant-based foods, not so much the effects of replacing it with chicken which is what the per capita consumption changes so more there
There are of course a number of other factors indeed that influence diabetes, yes
- usernamesAreTricky@lemmy.mlto
 ·1 year ago
·1 year agoThey also account for weight in the study, the association is still there after that's accounted for
See this response earlier in the thread from another commentor https://midwest.social/comment/3882967
- usernamesAreTricky@lemmy.mlto
 ·1 year ago
·1 year agoFrom the article
On the contrary, most people don’t read the educational plaques at zoos, and according to polls of zoo-goers, most go to spend time with friends or family — to enjoy themselves and be entertained, not to learn about animals and their needs. One study found the level of environmental concern reported by attendees before they entered the zoo was similar to those who were polled at the exits.
- usernamesAreTricky@lemmy.mlto
 ·1 year ago
·1 year agoFrom the article
On the contrary, most people don’t read the educational plaques at zoos, and according to polls of zoo-goers, most go to spend time with friends or family — to enjoy themselves and be entertained, not to learn about animals and their needs. One study found the level of environmental concern reported by attendees before they entered the zoo was similar to those who were polled at the exits.
- usernamesAreTricky@lemmy.mlto
 ·1 year ago
·1 year agoYet zoos also kill perfectly healthy creatures, however, because they are seen as "surplus"
So it's not like they are being just held there while they are healing and then released once they are healed
https://www.bbc.com/news/magazine-26356099
- usernamesAreTricky@lemmy.mlto
 ·1 year ago
·1 year agoFeed additives don't change overall methane emissions much, and not at all near what's touted by grossly misleading stats
What’s more, feeding cattle algae is really only practical where it’s least needed: on feedlots. This is where most cattle are crowded in the final months of their 1.5- to 2-year lives to rapidly put on weight before slaughter. There, algae feed additives can be churned into the cows’ grain and soy feed. But on feedlots, cattle already belch less methane—only 11 percent of their lifetime output
[...]
Unfortunately, adding the algae to diets on the pasture, where it’s most needed, isn’t a feasible option either. Out on grazing lands, it’s difficult to get cows to eat additives because they don’t like the taste of red algae unless it’s diluted into feed. And even if we did find ways to sneak algae in somehow, there’s a good chance their gut microbes would adapt and adjust, bringing their belches’ methane right back to high levels.
[...] All told, if we accept the most promising claims of the algae boosters, we’re talking about an 80 percent reduction of methane among only 11 percent of all burps—roughly an 8.8 percent reduction total
https://www.wired.com/story/carbon-neutral-cows-algae/
- usernamesAreTricky@lemmy.mlto
 ·1 year ago
·1 year agoI gave one in my comment? There's a quote with a source there















Yep for those curious how it harms native bees:
Also some fun facts: most North American native bee species don't even live in hives or produce honey for themselves at all. They also almost never sting too
https://www.nwf.org/Home/Magazines/National-Wildlife/2021/June-July/Gardening/Honey-Bees